 The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) measures illness and injury by using an acronym called DART. DART stands for “Days Away, Restricted and Transferred.” Companies use a formula designed by OSHA to calculate their DART. The variables used in this formula come from the company’s OSHA 300 form. The OSHA 300 form is used to track recordable injuries and illnesses within a given company in a given year.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) measures illness and injury by using an acronym called DART. DART stands for “Days Away, Restricted and Transferred.” Companies use a formula designed by OSHA to calculate their DART. The variables used in this formula come from the company’s OSHA 300 form. The OSHA 300 form is used to track recordable injuries and illnesses within a given company in a given year.
Tag: safety
Back-to-School Safety
 When summer comes to an end, children get ready to go back to school. This is a great time for parents to talk to their kids about how to safely travel to and from school. Following a few safety tips can help prevent children from suffering serious injuries.
When summer comes to an end, children get ready to go back to school. This is a great time for parents to talk to their kids about how to safely travel to and from school. Following a few safety tips can help prevent children from suffering serious injuries.
School Bus Safety Tips
- Children riding the bus to school should learn and practice a few safety rules for getting on and off the bus.
- Get to the bus stop early. Do not run to the bus.
- Wait until the bus has come to a complete stop before walking toward it.
- If crossing the street, wait for a signal from the bus driver. Look both ways to make sure there is no moving traffic from either direction.
- Always cross in front of the bus so the driver can see you.
- If the bus has lap and shoulder belts, use them.
- Once the bus is in motion, remain in your seat.
- If the window is open, keep your arms and head inside the bus at all times.
- Do not stand up to get off the bus until it has completely stopped.
- Only get off the bus at your assigned spot.
Walking Safety Tips
- Children should only walk to school alone if they are old enough and ready to make the walk safely.
- Children are not ready to walk to school without an adult until they are at least 10 years old.
- Younger kids cannot be trusted to make smart traffic choices on their own.
- Plan and practice a safe walking route with your child until she knows it well.
- Use streets with sidewalks, crosswalks and crossing guards. Avoid as many intersections as possible.
- Have children walk with a friend or in a group.
- Talk to your child about what to do if they are approached by a stranger.
Safety Tips for Drivers
- Drivers should be aware of children walking to school or to the bus stop. Everyone can follow a few safety tips to help kids get to school safely.
- When backing out of the driveway, watch for children walking to school or to a bus stop.
- On streets without crossing guards, watch out for children trying to cross the street.
- Be careful on streets without sidewalks or streets with on-street parking. It might be hard to notice a child behind a car.
- Be alert. Children may dart into the street without looking.
- Slow down.
via Injury Research and Policy Back-to-School Safety :: Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio.
Hand and Power Tool Safety
 Hand and power tools are a common part of our everyday lives and are present in nearly every industry. These tools help us to easily perform tasks that otherwise would be difficult or impossible. However, these simple tools can be hazardous and have the potential for causing severe injuries when used or maintained improperly. Special attention toward hand and power tool safety is necessary in order to reduce or eliminate these hazards.
Hand and power tools are a common part of our everyday lives and are present in nearly every industry. These tools help us to easily perform tasks that otherwise would be difficult or impossible. However, these simple tools can be hazardous and have the potential for causing severe injuries when used or maintained improperly. Special attention toward hand and power tool safety is necessary in order to reduce or eliminate these hazards.
Walking Safety Rules
 Walk Facing Traffic: If there is no sidewalk and you must walk on the side of the road, choose the side where you are facing oncoming traffic. In North America, this is the left side of the road. This gives you the best chance to see traffic approaching closest to you and take evasive action when needed.
Walk Facing Traffic: If there is no sidewalk and you must walk on the side of the road, choose the side where you are facing oncoming traffic. In North America, this is the left side of the road. This gives you the best chance to see traffic approaching closest to you and take evasive action when needed.- Cross Safely: Mom was right: look both ways before crossing any street. At controlled intersections, it is wise to cross only when you have the pedestrian crossing light, but even then, drivers and bikers may have a green light to turn and won’t be expecting you to be in the crosswalk. Make eye contact with any drivers who may be turning. Give them a wave. Make sure they see you. In a car-walker interaction, you can only lose.
- Walk Single File: Unless you are on a sidewalk separated from the road or a wide bike lane, you should walk in single file. This is especially important on a road with lots curves, where traffic has only a split second chance of seeing you before hitting you. While it can be enjoyable to walk down the road two to three abreast chatting merrily, drivers don’t expect it and you may lose your best walking buddies.
- Stay Aware of Bikes and Runners: Share the road and path with bikes and runners. Bike riders should alert you when approaching from behind with a bike bell or a “passing on the left/right.” Listen for them, and move to walk single file, allowing them to pass safely. Runners should also call out for passing. Bike-walker collisions can result in broken bones or head injury for either — and you aren’t wearing a helmet.
- Be Visible: Wear bright colors when walking in daytime. When walking at night, wear light-colored clothing and reflective clothing or a reflective vest to be visible. Drivers are often not expecting walkers to be out after dark, and you need to give them every chance to see you, even at street crossings that have crossing signals. Be just as cautious at dawn or twilight, as drivers still have limited visibility or may even have the setting or rising sun directly in their eyes.
- Be Predictable: Make a practice of staying on one side of the path while walking rather than weaving randomly from side to side. Watch your arm motions, or you may end up giving a black eye to a silently passing walker, runner or biker.
- Keep the Volume Down: Don’t drown out your environment with your iPod. Keep the volume at a level where you can still hear bike bells and warnings from other walkers and runners. Your audiologist will also thank you.
- Hang Up and Walk: Chatting on a cell phone while you walk is as dangerous as chatting while driving. You are distracted and not as aware of your environment. You are less likely to recognize traffic danger, passing joggers and bikers or tripping hazards. Potential criminals see you as a distracted easy target.
- Walk Dogs on Short Leashes: I’ve seen many tragedies of dogs running out in to traffic or getting into a fatal dog fight either off leash or on a very long leash. Don’t trip up other walkers or bikers with poor control of your pet. Keep your pet and yourself safe by learning proper leash walking.
- Know When to Stop Walking: Heat sickness, dehydration, heart attack or stroke can strike walkers of any age. Learn the symptoms of medical emergencies and carry a cell phone to dial 911.
- Be Aware of Stranger Danger: Choose your walking route for paths frequented by other walkers, joggers and bikers. If you see someone suspicious, be prepared to alter your course or go in to a store or public building to avoid them. Acting alert and aware can convince bad guys to choose an easier target.
via Walking Safety Rules.
Motor Vehicle Safety on The Job
 Risk of work-related motor vehicle crashes cuts across all industries and occupations. Workers who drive on the job may be “professional” drivers whose primary job is to transport freight or passengers. Many other workers spend a substantial part of the work day driving a vehicle owned or leased by their employer, or a personal vehicle. In the United States, companies and drivers that operate large trucks and buses are covered by comprehensive safety regulations. In contrast, there are no Federal occupational safety regulations that cover the workers who use smaller employer-provided vehicles or personal vehicles.
Risk of work-related motor vehicle crashes cuts across all industries and occupations. Workers who drive on the job may be “professional” drivers whose primary job is to transport freight or passengers. Many other workers spend a substantial part of the work day driving a vehicle owned or leased by their employer, or a personal vehicle. In the United States, companies and drivers that operate large trucks and buses are covered by comprehensive safety regulations. In contrast, there are no Federal occupational safety regulations that cover the workers who use smaller employer-provided vehicles or personal vehicles.
For all workers who drive on the job, employer safety policies are a critical element in reducing crash risks. Employer policies may be limited to supporting and reinforcing state traffic laws. However, many employers choose to manage road risk more proactively through programs and policies to promote safe driving behaviors, ensure that work-related driving takes place under the safest possible conditions, and ensure that worker vehicles are safe and properly maintained.
via CDC – Motor Vehicle Safety – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic.
Raising Awareness About Electric Shock Drowning
 Conscientious parents, who would never imagine letting their children go boating without a life vest or ride in a car without securing their seat belts, often have no qualms about letting a child jump off a dock into fresh water. What these parents don’t realize is that if the dock has120-volt AC power, lethal amounts of electricity could be finding their way into the water from faulty wiring on the dock or a boat. In a one-week period this past July, four children and one young adult were killed in separate electric shock drowning (ESD) incidents at docks on freshwater lakes.
Conscientious parents, who would never imagine letting their children go boating without a life vest or ride in a car without securing their seat belts, often have no qualms about letting a child jump off a dock into fresh water. What these parents don’t realize is that if the dock has120-volt AC power, lethal amounts of electricity could be finding their way into the water from faulty wiring on the dock or a boat. In a one-week period this past July, four children and one young adult were killed in separate electric shock drowning (ESD) incidents at docks on freshwater lakes.
via BoatUS: Seaworthy Magazine: Raising Awareness About Electric Shock Drowning | October ’12.
Electrical Safety
 Electrical current exposes workers to a serious, widespread occupational hazard; practically all members of the workforce are exposed to electrical energy during the performance of their daily duties, and electrocutions occur to workers in various job categories. Many workers are unaware of the potential electrical hazards present in their work environment, which makes them more vulnerable to the danger of electrocution.Electrical injuries consist of four main types: electrocution fatal, electric shock, burns, and falls caused as a result of contact with electrical energy.
Electrical current exposes workers to a serious, widespread occupational hazard; practically all members of the workforce are exposed to electrical energy during the performance of their daily duties, and electrocutions occur to workers in various job categories. Many workers are unaware of the potential electrical hazards present in their work environment, which makes them more vulnerable to the danger of electrocution.Electrical injuries consist of four main types: electrocution fatal, electric shock, burns, and falls caused as a result of contact with electrical energy.
via CDC – Electrical Safety – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic.
SKATEBOARD, SCOOTER, IN-LINE SKATING SAFETY
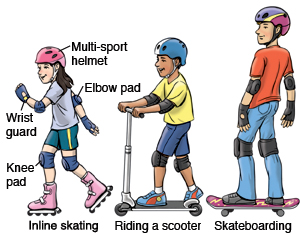 All skateboarders and scooter-riders should wear protective gear; helmets are particularly important for preventing and minimizing head injuries. Riders should wear helmets that meet ASTM or other approved safety standards, and that are specifically designed to reduce the effects of skating hazards.
All skateboarders and scooter-riders should wear protective gear; helmets are particularly important for preventing and minimizing head injuries. Riders should wear helmets that meet ASTM or other approved safety standards, and that are specifically designed to reduce the effects of skating hazards.- Communities should continue to develop skateboard parks, which are more likely to be monitored for safety than ramps and jumps constructed by children at home.
- While in-line skating or using Heelys, only skate on designated paths or rinks and not in the street.
- Most accidents occur due to falls. Inexperienced riders should only ride as fast as they can comfortably slow down, and they should practice falling on grass or other soft surfaces. Before riding, skateboarders should survey the riding terrain for obstacles such as potholes, rocks, or any debris.
- Children should never ride skateboards or scooters in or near moving traffic.
- Riders should never skate alone. Children under the age of eight should be closely supervised at all times.
via Summer Safety Tips.
Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs)
Approximately 890 deaths from coronary heart disease occur outside of the hospital or emergency room every day. Most of these deaths are due to the sudden loss of heart function or sudden cardiac death.1 In 2001 and 2002, there were 6628 workplace fatalities reported to OSHA; 1216 from heart attack, 354 from electric shock, and 267 from asphyxia. A number of these victims, up to 60 percent, might have been saved if automated external defibrillators (AEDs) were immediately available. Chances of survival from sudden cardiac death diminish by 7 – 10 percent for each minute without immediate CPR or defibrillation. After 10 minutes, resuscitation rarely succeeds. An AED is an electronic device designed to deliver an electric shock to a victim of sudden cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation may be restored to normal rhythm up to 60 percent of the time if treated promptly with an AED, a procedure called defibrillation.
via Safety and Health Topics | Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs).
The 10 most dangerous jobs in America
 According to a September report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics BLS, fisherman, loggers and pilots were the three deadliest in the United States in 2011. The organization recently examined the occupations with the highest rate of work-related deaths and found that of all U.S. workers, fishermen are the most likely to die on the job.
According to a September report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics BLS, fisherman, loggers and pilots were the three deadliest in the United States in 2011. The organization recently examined the occupations with the highest rate of work-related deaths and found that of all U.S. workers, fishermen are the most likely to die on the job.
Here is the full list of work-related deaths in 2011 per 100,000 workers:
- Fisherman 121.2
- Loggers 102.4
- Pilots 57.0
- Farmers and Ranchers 25.3
- Police Officers 18.6
- Construction Workers 15.7
- National Average 3.5
- Firefighters 2.5
- Cashiers 1.6
- Office Admin 0.6
- Business and Finance Staff 0.5

