 More than a million Americans have heart attacks each year. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction (MI), is permanent damage to the heart muscle. “Myo” means muscle, “cardial” refers to the heart, and “infarction” means death of tissue due to lack of blood supply. via Heart Attack – WebMD: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More.
More than a million Americans have heart attacks each year. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction (MI), is permanent damage to the heart muscle. “Myo” means muscle, “cardial” refers to the heart, and “infarction” means death of tissue due to lack of blood supply. via Heart Attack – WebMD: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More.
Category: Wellness
The Medical Cost of Obesity
 Study Estimates Medical Cost of Obesity May Be As High as $147 Billion Annually
Study Estimates Medical Cost of Obesity May Be As High as $147 Billion Annually
The health cost of obesity in the United States is as high as $147 billion annually, based on a new study from RTI and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The study which appears online today in the journal Health Affairs, was released at CDC’s Weight of the Nation conference in Washington, DC.
The proportion of all annual medical costs that are due to obesity increased from 6.5 percent in 1998 to 9.1 percent in 2006, the study said. This total includes payment by Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers, and includes prescription drug spending. Overall, persons who are obese spent $1,429 (42 percent) more for medical care in 2006 than did normal weight people. These estimates were compiled using national data that compare medical expenses for normal weight and obese persons.
What is a Concussion?
 A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury, or TBI, caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head that can change the way your brain normally works. Concussions can also occur from a fall or a blow to the body that causes the head and brain to move quickly back and forth.
A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury, or TBI, caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head that can change the way your brain normally works. Concussions can also occur from a fall or a blow to the body that causes the head and brain to move quickly back and forth.
Health care professionals may describe a concussion as a “mild” brain injury because concussions are usually not life-threatening. Even so, their effects can be serious.
via CDC – Concussion – Traumatic Brain Injury – Injury Center.
The Benefits of Physical Activity
 Regular physical activity is one of the most important things you can do for your health. It can help:
Regular physical activity is one of the most important things you can do for your health. It can help:
- Control your weight
- Reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease
- Reduce your risk for type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome
- Reduce your risk of some cancers
- Strengthen your bones and muscles
- Improve your mental health and mood
- Improve your ability to do daily activities and prevent falls, if you’re an older adult
- Increase your chances of living longer
via Physical Activity for Everyone: The Benefits of Physical Activity | DNPAO | CDC.
Youth Sports Safety: Your Child
 What do I need to know about kids and sports injuries?
What do I need to know about kids and sports injuries?
Playing sports is a great way for your child to stay fit and healthy, to learn about teamwork, make friends, and develop a sense of personal satisfaction. In addition, taking part in youth sports may lead to greater leisure-time physical activity as an adult.
However, kids’ injuries from playing sports are on the rise, perhaps due to several factors:
- Physical stress from the demands of training on kids’ growing bodies
- Life stress (which increases the risk of injury)
- Improper training
- Poor coaching
Can youth sports injuries be prevented?
Most sports injuries can be prevented, even predicted! The first step in preventing sports injuries is finding out why sports injuries occur. Sports injuries may be caused by:
- Individual risk factors (such as medical conditions)
- Inadequate physical exams before participating (every child should get a sports-specific physical exam before each season)
- Find out what experts say about heart screening for young athletes.
- Lack of pre-season conditioning
- Lack of safety equipment, or poorly fitted, improper equipment
- Lack of proper eye protection
- Teaming up by age instead of size
- Unsafe playing fields, or surfaces
- Improper training or coaching, or lack of instruction
- Fatigue
- Not warming up, cooling down and stretching properly
- Playing while injured
- Stress and inappropriate pressure to win
- Temperature
- Poor nutrition or hydration
via Youth Sports Safety: Your Child: University of Michigan Health System.
Avoid Hepatitis C Virus
 Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis C virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis C is usually spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. Today, most people become infected with the Hepatitis C virus by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs. Before 1992, when widespread screening of the blood supply began in the United States, Hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants.Hepatitis C can be either “acute” or “chronic.” Acute Hepatitis C virus infection is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the Hepatitis C virus. For most people, acute infection leads to chronic infection. Chronic Hepatitis C is a serious disease than can result in long-term health problems, or even death.There is no vaccine for Hepatitis C. The best way to prevent Hepatitis C is by avoiding behaviors that can spread the disease, especially injection drug use.
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis C virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis C is usually spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. Today, most people become infected with the Hepatitis C virus by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs. Before 1992, when widespread screening of the blood supply began in the United States, Hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants.Hepatitis C can be either “acute” or “chronic.” Acute Hepatitis C virus infection is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the Hepatitis C virus. For most people, acute infection leads to chronic infection. Chronic Hepatitis C is a serious disease than can result in long-term health problems, or even death.There is no vaccine for Hepatitis C. The best way to prevent Hepatitis C is by avoiding behaviors that can spread the disease, especially injection drug use.
Eat Your Fruits and Vegetables
 “Eat your fruits and vegetables.” You’ve likely heard this statement since childhood. Research shows why it is good advice:
“Eat your fruits and vegetables.” You’ve likely heard this statement since childhood. Research shows why it is good advice:
Healthy diets rich in fruits and vegetables may reduce the risk of cancer and other chronic diseases. Fruits and vegetables also provide essential vitamins and minerals, fiber, and other substances that are important for good health. Most fruits and vegetables are naturally low in fat and calories and are filling.
via Nutrition for Everyone: Fruits and Vegetables | DNPAO | CDC.
MRSA and the Workplace
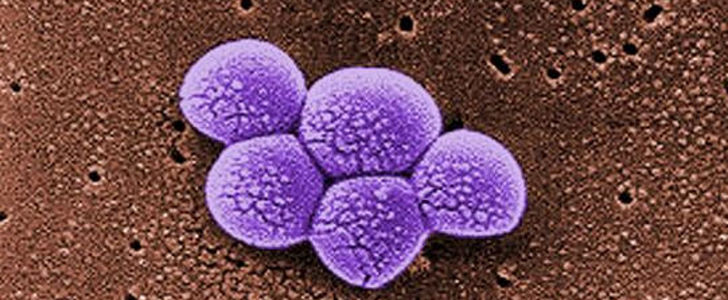 Staphylococcus aureus, often referred to simply as “staph,” is a type of bacteria commonly carried on the skin or in the nose of healthy people. Sometimes, staph can cause an infection. Staph bacteria are one of the most common causes of skin infections in the United States. Most of these skin infections are minor such as pustules and boils and can be treated without antibiotics. However, staph bacteria also can cause serious infections such as surgical wound infections, bloodstream infections, and pneumonia.
Staphylococcus aureus, often referred to simply as “staph,” is a type of bacteria commonly carried on the skin or in the nose of healthy people. Sometimes, staph can cause an infection. Staph bacteria are one of the most common causes of skin infections in the United States. Most of these skin infections are minor such as pustules and boils and can be treated without antibiotics. However, staph bacteria also can cause serious infections such as surgical wound infections, bloodstream infections, and pneumonia.
via CDC – MRSA and the Workplace – NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic.
Key Facts About Patient Safety
What do we mean when we talk about patient safety?
 Doctors, nurses, and other health professionals dedicate their lives to caring for their patients. But providing health care can be complicated. There are often multiple steps involved in a health care visit. A number of different medical staff may be take part in the care of a single patient. And patients may be confused by unfamiliar words and technical language.Although hospitals, clinics, and doctor’s offices take many steps to keep their patients safe, medical errors can happen. Often, medical errors also called adverse events happen when there is a single misstep in a chain of activities.
Doctors, nurses, and other health professionals dedicate their lives to caring for their patients. But providing health care can be complicated. There are often multiple steps involved in a health care visit. A number of different medical staff may be take part in the care of a single patient. And patients may be confused by unfamiliar words and technical language.Although hospitals, clinics, and doctor’s offices take many steps to keep their patients safe, medical errors can happen. Often, medical errors also called adverse events happen when there is a single misstep in a chain of activities.
via Key Facts About Patient Safety | National Patient Safety Foundation.
Avoid Exposure to Bloodborne Infectious Diseases
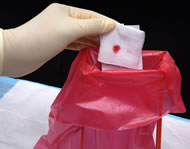 Exposures to blood and other body fluids occur across a wide variety of occupations. Health care workers, emergency response and public safety personnel, and other workers can be exposed to blood through needlestick and other sharps injuries, mucous membrane, and skin exposures. The pathogens of primary concern are the human immunodeficiency virus HIV, hepatitis B virus HBV, and hepatitis C virus HCV. Workers and employers are urged to take advantage of available engineering controls and work practices to prevent exposure to blood and other body fluids.
Exposures to blood and other body fluids occur across a wide variety of occupations. Health care workers, emergency response and public safety personnel, and other workers can be exposed to blood through needlestick and other sharps injuries, mucous membrane, and skin exposures. The pathogens of primary concern are the human immunodeficiency virus HIV, hepatitis B virus HBV, and hepatitis C virus HCV. Workers and employers are urged to take advantage of available engineering controls and work practices to prevent exposure to blood and other body fluids.
